Contents
- 1. Caoutchouc
- 2. Dépaysant
- 3. Métro-boulot-dodo
- 4. Flâner
- 5. Yaourter
- 6. Frappadingue
- 7. Loufoquerie
- 8. Hurluberlu
- 9. Tohu-bohu
- 10. Râler
- 11. Œil-de-bœuf
- 12. Chauve-souris
- 13. Cerf-volant
- 14. Crapoter
- 15. Spleen
- 16. Saperlipopette
- 17. Balles
- 18. Fute-fute
- 19. Prout
- 20. Raplapla
- 21. Anticonstitutionnellement
- And One More Thing...
21 Weird French Words

Linguists remain at odds as to whether the language we speak influences how we think or vice versa. However you choose to look at it, though, some languages are just full of words that can seem strange to a non-native speaker, and French is no exception.
Advanced learners may be amused to learn some of these words, and anyone with an interest in French will see how some of these words aren’t the cognates their spellings may have you believe they are at first glance.
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
1. Caoutchouc
This word means “rubber,” as in the bendy substance we get from trees, and actually has a fairly straightforward history. Caoutchouc comes from the native South American language Quechua and its word kawchu. Indeed English is the “odd one out” when it comes to this word, because the German Kautschuk and the Spanish caucho have the same origins.
2. Dépaysant
Dépaysant, directly translated, means “un-country-ing.” A strange word, to say the least, but one that expresses a sentiment similar to homesickness. It’s the feeling you get when you’re in a new place and experiencing very new things that make you feel foreign, out of sorts and strange. Eating dinner at 9 p.m. in the south of France might be dépaysant, or giving new friends the bise (greeting them by kissing on the cheek).
3. Métro-boulot-dodo
Métro refers to public transportation, boulot to the slang term for a job and dodo to baby talk for “sleep” (akin to “sleepytime” or “beddy-bye”). Smash it all together, though, and you have a French compound noun that sums up the existential quandary of adult life: commute-job-sleep. Now say it 10 times fast, pass out and wake up for work tomorrow. No time to read Camus, you’re all grown up!
4. Flâner
This Baudelarian term is perfectly suited to French culture. Flâner is to wander with no particular destination in mind, people watching, window shopping and basically existing as a city-dweller. To Baudelaire’s mind, this sort of wandering was perfectly suited to a city like Paris, and he wrote many of his prose poems about doing just this—wandering. It makes sense, then, that a flâneur (or flâneuse, for a woman), is someone who spends a good amount of time wandering about.
5. Yaourter
Literally “to yogurt,” yaourter describes singing or speaking in a language one either doesn’t know very well or has decided to fake in whatever context they’re using it. Common usage refers to more of an imitation than a sincere attempt, like trying to fudge your way through a song you haven’t memorized the lyrics to, or speaking a “pretend” language by mimicking the accent and vocal mannerisms without using real words.
Another way to describe this phenomenon is with the expression chanter en yaourt (to sing through yogurt). Either term is often used to refer to a native French speaker singing along with English words with which they’re not entirely familiar.
6. Frappadingue
This fantastic, hybrid word is great for telling someone just how crazy they really are. Frappadingue comes from two separate words that both point towards someone’s insanity. Frappé- is the first part and comes from the verb frapper (to hit), as in, “You’re so nuts you must have been hit on the head.”
7. Loufoquerie
Loufoquerie is a word for “craziness.” The French word loufoque originated from fou (standard French for “crazy”) in louchébem (a slang invented by French butchers in the 19th century).
Louchébem involves moving the first consonant of a word to the end, tacking on a standard suffix and adding the letter “L” to the beginning. This is still used in the French meat industry today. I don’t know how these things are true, they just are. You can’t possibly hold me responsible for this loufoquerie!
8. Hurluberlu
Hurluberlu can be used to describe an eccentric, scatterbrained person—like a crackpot or screwball. In other words, someone who might from time to time engage in some loufoquerie.
The exact origins of this word are unknown, but it’s old enough to have been used in the 16th century by the French Renaissance writer François Rabelais. Rabelais was playful and creative with his word choice and highly influential on the French language. He was responsible for adding loan words to French from Greek and Latin, as well as making up some of his own, so it’s impossible to know from exactly whence hurluberlu was plucked.
9. Tohu-bohu
This is a loan word taken from the Hebrew tohu wa-bohu, which appears in the original text of the Bible in the Book of Genesis, referring to the formless state of the universe before God created light, water, animals, people, etc.
So practically the same word that was used to describe the origins of time can now be used to describe what happens when two car alarms go off simultaneously in a parking lot between a senior bingo game and a folk concert: confusion, pandemonium.
10. Râler
Râler describes a very particular way of complaining that has been all but perfected by the French. Somewhat more distinguished than whining, but not nearly as precise as complaining, râler is how the French express their perpetual dissatisfaction with the world. It is done with utmost grace, poise and perfect grammar, bien sûr.
11. Œil-de-bœuf
You may be familiar with this word already since it has been adopted into English much in the same way as hors-d’œuvre. Œil-de-bœuf literally translates to “ox eye,” but luckily does not refer to something edible. Rather, œil-de-bœuf refers to an oculus, or a circular/oval window often part of the architecture of churches, mosques and castles. In fact, the word œil (eye) can be used in French architectural lingo to refer to any small opening. This is logical though, since the English term “oculus” is also simply borrowed from the Latin word for “eye.”
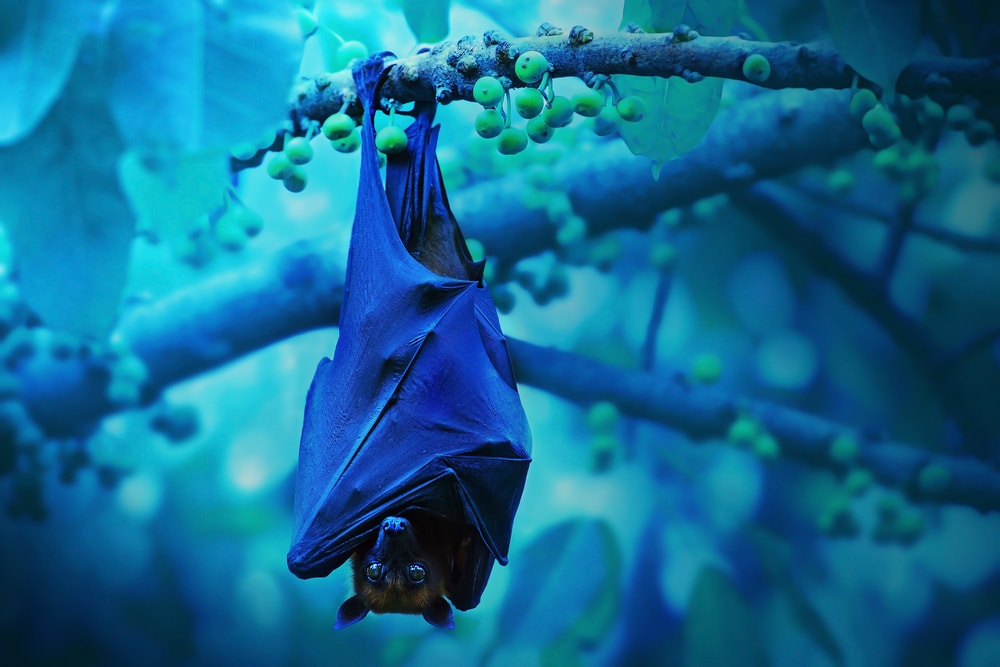
12. Chauve-souris
The word chauve-souris means “bat”. You may recognize the two composing parts of this word on their own: chauve means “bald” and souris means “mouse.” There is a bit of debate among linguists as to how the so very strange chauve-souris came to replace the Latin term vespertilio. The most common theory is that folks used to call bats “owl mice” in popular Latin. The word for owl (cavannus) somehow got confused with the word for bald (calvus), and the rest is history!
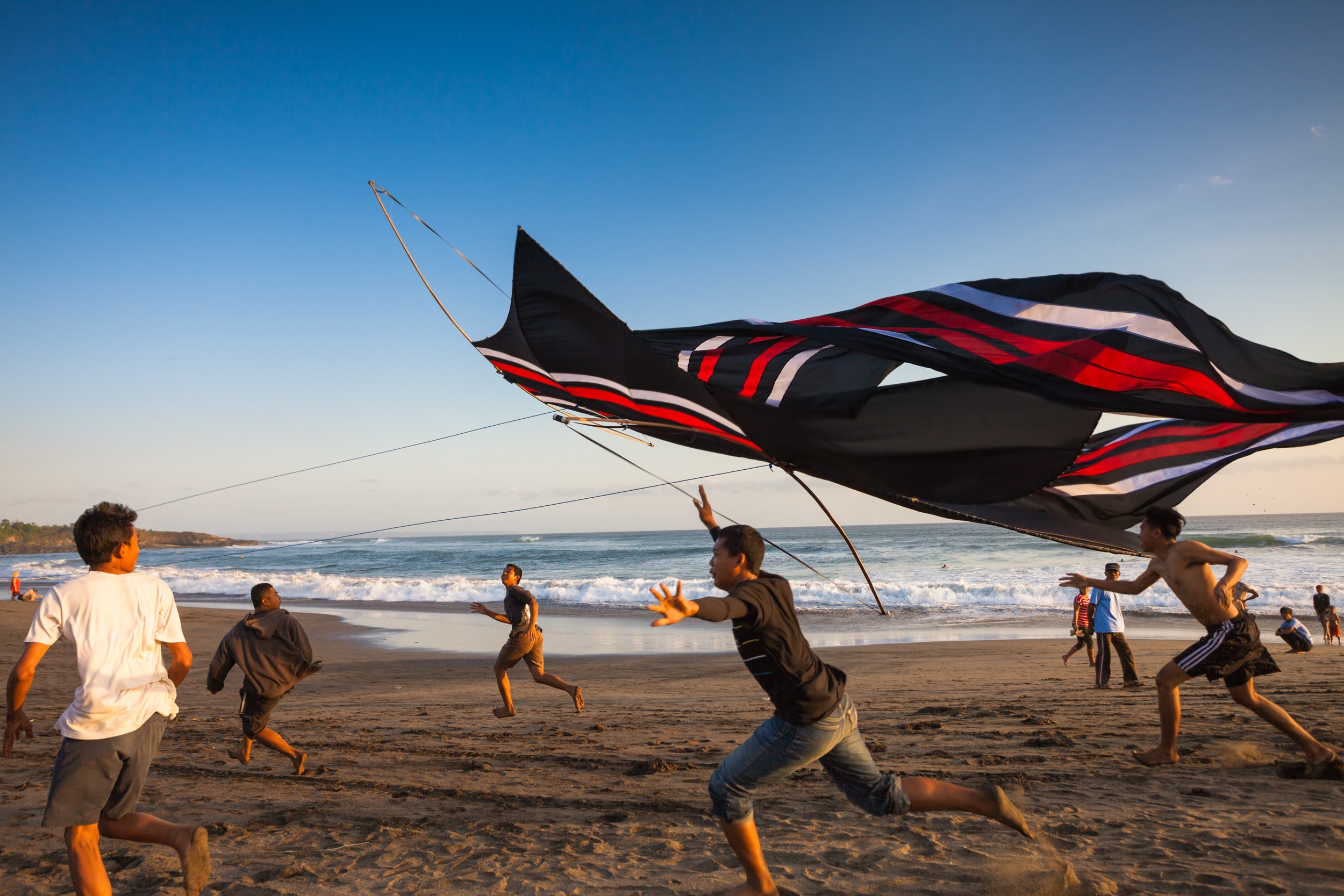
13. Cerf-volant
Cerf-volant literally translates to “flying deer.” Contrary to what every French learner hopes when trying to decipher this word for the first time, a cerf-volant is not a mythical creature floating about the forests of France alongside Merlin the magician! Take heart, however, because it is still a rather whimsical word, referring to a kite.
Like chauve-souris, there has been some debate about the origin of cerf-volant. It’s generally agreed that the term unfortunately has nothing to do with flying deer, but comes from a mistaken spelling of the Old French serp-volante, under the influence of Occitan—a language spoken in the south of France. The word serp referred to another creature, of course: a serpent or dragon.
14. Crapoter
The French have actually invented a word for an amateur’s tendency to puff smoke without really getting a lungful.
When you think about it, crapoter is similar in spirit to yaourter, in that both words are used to refer to people who have chosen to pretend, or faire semblant. Perhaps these words reveal a particular disdain the French have for fakers, or perhaps they just reveal a French propensity for making stuff up.
15. Spleen
Another Baudelarian term, this word has nothing to do with the organ, which is called the rate in French. Spleen is a sentiment linked with profound feelings of dissatisfaction and discouragement. Take another typical French expression, ennui, and multiply it to the nth degree to get spleen. For Baudelaire, spleen became so overwhelming and pressing that he wrote several prose poems dedicated entirely to this feeling.
16. Saperlipopette
Saperlipopette falls into the category of expressions most people don’t say sincerely these days, or can’t even believe were ever said sincerely. You might have said this word if you stubbed your toe, were surprised by someone or if you were just angry and needed to yell something non-vulgar. Saperlipopette appears in an early essay of the French poet Rimbaud.
17. Balles
Balles means bullets, but if you hear someone use this term in a market, weapons are probably not involved. That’s because it’s also a street term for euros. In the United States, it would be the equivalent of hearing “bucks”; you’re not talking about male deer, but rather dollars. If you want to sound really authentic, use balles when you’re emphatically complaining about how expensive something is!
18. Fute-fute
The French are big on repeated syllables, which has resulted in amusing words from chouchou (a term of endearment) to kif-kif (an Arab loan word meaning “all the same”), but this one is my personal favorite.
Meaning clever or bright, fute-fute is commonly used in the negative phrase pas fute-fute, to indicate that someone is not (as we might say in English) the brightest bulb in the box. A slang version of the adjective futé, meaning clever or cunning, fute-fute is especially lovable for its onamonapoetic evocation of a short circuit. You can just see the light bulb over the head flickering out!
19. Prout
Prout is the onomatopoetic word for “toot” in French and it acts in much the same way—turning flatulence into childish joy and ROTFL-type laughter, as well as accurately describing the noise a horn makes. Onomatopoetic words are often fun, but this one in particular seems to have a special… shall we say, charm, in any language!
20. Raplapla
The word raplapla in French means “limp” or “flabby.” It is often used to describe something that is lacking energy, strength, or vitality, like a tired or weak person, or something that is deflated or sagging. It can also be used figuratively to describe a situation that feels lackluster or unexciting.
21. Anticonstitutionnellement
The word anticonstitutionnellement, the longest in French, means “unconstitutionally.” It originates from the noun “constitution” and the prefix “anti-,” denoting opposition. It is typically used to describe actions or behaviors that go against the principles or provisions of a constitution. You’ll usually find this word in legal or political contexts, where discussions revolve around the violation or disregard of constitutional rights, laws, or processes.
FluentU takes authentic videos—like music videos, movie trailers, news and inspiring talks—and turns them into personalized language learning lessons.
You can try FluentU for free for 2 weeks. Check out the website or download the iOS app or Android app.
P.S. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)
As you can see, French has a lot of odd words to learn.
These words have probably been a lot to process. But if you do have that drained, collapsed feeling, you should have no problem remembering the word raplapla, which is used to refer to a tired or worn out state but is also believed to be connected to the word plat (flat). Ever driven on a flat tire? Exactly.
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
And One More Thing...
If you like learning French at your own pace and from the comfort of your device, I have to tell you about FluentU.
FluentU makes it easier (and way more fun) to learn French by making real content like movies and series accessible to learners. You can check out FluentU's curated video library, or bring our learning tools directly to Netflix or YouTube with the FluentU Chrome extension.
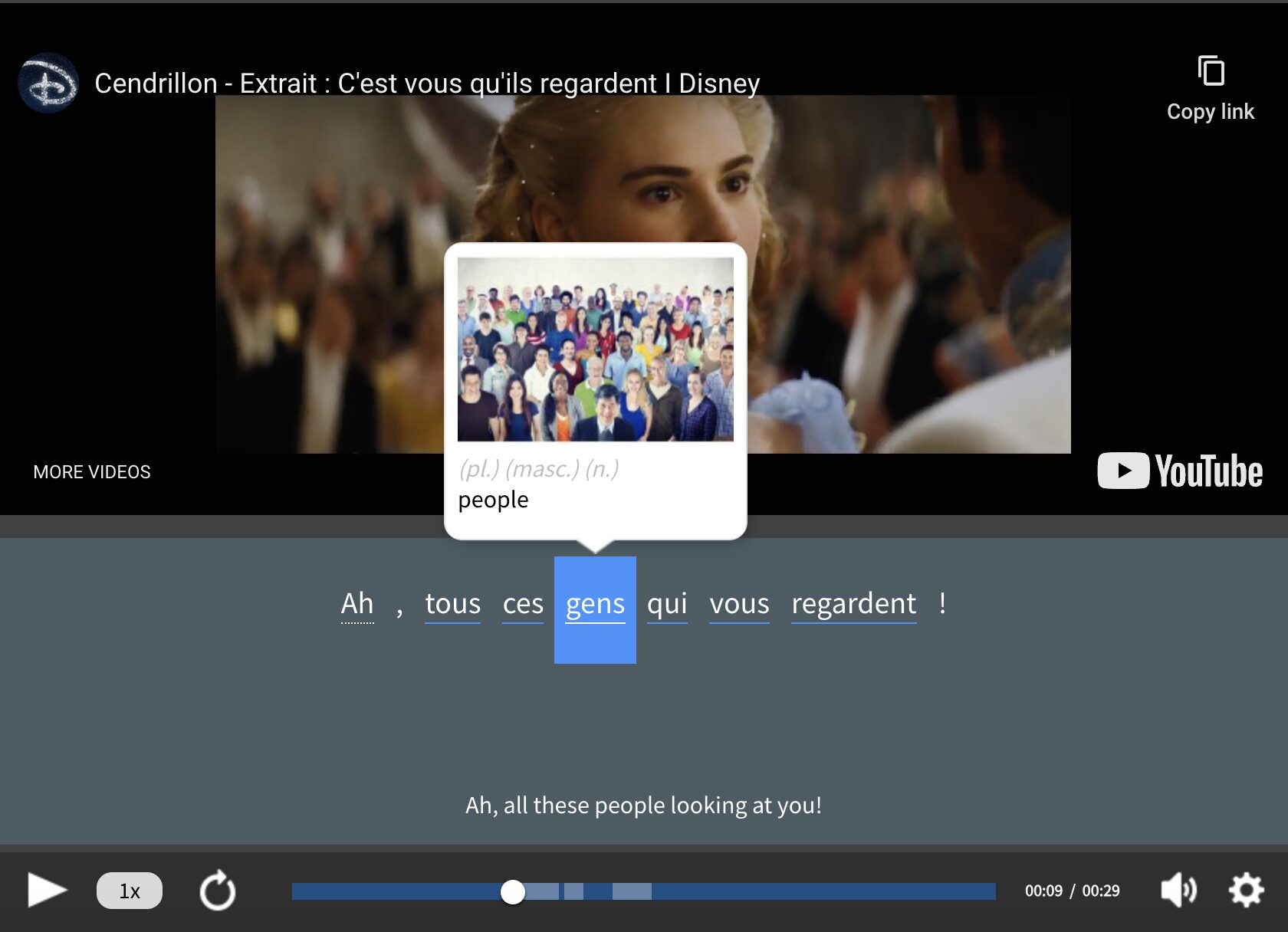
One of the features I find most helpful is the interactive captions—you can tap on any word to see its meaning, an image, pronunciation, and other examples from different contexts. It’s a great way to pick up French vocab without having to pause and look things up separately.
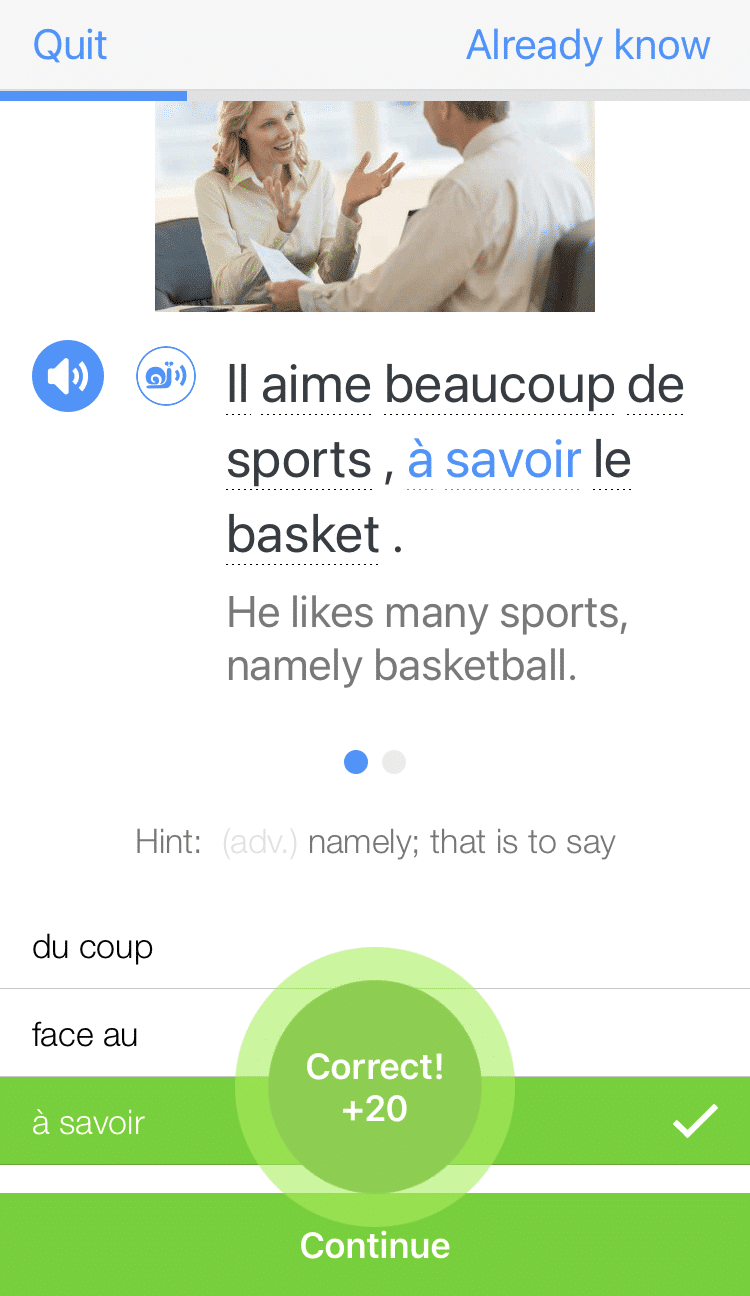
FluentU also helps reinforce what you’ve learned with personalized quizzes. You can swipe through extra examples and complete engaging exercises that adapt to your progress. You'll get extra practice with the words you find more challenging and even be reminded you when it’s time to review!
You can use FluentU on your computer, tablet, or phone with our app for Apple or Android devices. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)