Essere vs. Avere: When to Use Them

As two of the most common—and arguably most important—verbs in the Italian language, essere and avere are used in a wide variety of ways and serve as a grammatical aid in many situations.
They’re commonly in their present tense form to mean “to be” (essere) and “to have” (avere). But they’re also used to create compound tenses, such as the passato prossimo (the present perfect tense) and the trapassato prossimo (the past perfect tense).
Finally, these two verbs can be used in idiomatic expressions that extend their functions beyond their basic translations.
Let’s dive in a little deeper with these Italian verbs.
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
The Conjugations of Essere and Avere
While these two verbs end in -ere (a regular verb ending), they are, in fact, irregular in the present tense. Not to worry, though: once you learn them, they can be used practically everywhere!
Check out their full conjugations in the present tense:
Essere in the Present Tense
| Italian | English Translation |
|---|---|
| Io sono felice. | I am happy. |
| Tu sei triste. | You are sad. |
| Lui è un avvocato. | He is a lawyer. |
| Lei è italiana. | She is Italian. |
| Noi siamo in un ristorante. | We are in a restaurant. |
| Voi siete francesi. | You all are French. |
| Loro sono di Milano. | They are from Milan. |
Avere in the Present Tense
| Italian | English Translation |
|---|---|
| Io ho un libro. | I have a book. |
| Tu hai un esame? | Do you have an exam? |
| Lui ha un po' di vino. | He has a little wine. |
| Lei ha una forchetta. | She has a fork. |
| Noi abbiamo qualcosa da dire. | We have something to say. |
| Voi avete dei fidanzati? | Do you all have boyfriends? |
| Loro hanno le chiavi. | They have the keys. |
In other tenses, conjugating essere and avere is a little bit simpler to remember. While both have irregular stems for other tenses such as imperfetto (imperfect) and il futuro semplice (future simple), they follow the almost same conjugation patterns.
For example, in the imperfect, avere uses the stem av- and adds the regular -ere verb endings, but essere is completely irregular. Check them out!
Essere in the Imperfect
| Italian | English Translation |
|---|---|
| Io ero | I was |
| Tu eri | You were |
| Lui era | He was |
| Lei era | She was |
| Noi eravamo | We were |
| Voi eravate | You all were |
| Loro erano | They were |
Avere in the Imperfect
| Italian | English Translation |
|---|---|
| Io avevo | I had |
| Tu avevi | You had |
| Lui aveva | He had |
| Lei aveva | She had |
| Noi avevamo | We had |
| Voi avevate | You all had |
| Loro avevano | They had |
In the future simple, essere uses the stem sar-, and avere uses the stem avr-. To these stems, regular conjugation endings are added.
Essere in the Future Simple
| Italian | English Translation |
|---|---|
| Io sarò | I will be |
| Tu sarai | You will be |
| Lui sarà | He will be |
| Lei sarà | She will be |
| Noi saremo | We will be |
| Voi sarete | You all will be |
| Loro saranno | They will be |
Avere in the Future Simple
| Italian | English Translation |
|---|---|
| Io avrò | I will have |
| Tu avrai | You will have |
| Lui avrà | He will have |
| Lei avrà | She will have |
| Noi avremo | We will have |
| Voi avrete | You all will have |
| Loro avranno | They will have |
Aside from these two tenses, the same stems for the futuro semplice are also used for the condizionale moods (present and past) as well as the futuro anteriore (the future perfect).
As for other other Italian past tenses, such as il passato prossimo (the present perfect), essere and avere have irregular past participles: essere uses stato and avere uses avuto . Both of these verbs take avere as an auxiliary in compound tenses.
Finally, in the congiuntivo (subjunctive), both verbs are highly irregular—but that is a subject for another post.
When to Use Essere
Outside of its simple meaning and use in compound tenses, essere is also used in fixed expressions.
It can be used to describe emotions such as anger, happiness, boredom, sadness or worry. It can also be used in idiomatic expressions to describe lateness, stubbornness and tiredness.
Check out these examples:
Mi scusi: sono in ritardo. (Excuse me: I am late.)
Mia sorella è molta testarda. (My sister is very stubborn.)
Loro non sono stanchi. (They are not tired.)
Note: contrary to what our English brains might assume, essere is not used to answer the question “come stai?” (“how are you?”). Instead, the verb stare is used for that:
Come stai? Bene, grazie! (How are you? Good, thanks!)
Further, essere is also used as a linking verb that connects subjects with adjectives (description words). When used like this, the adjective must agree in gender and number with the subject.
For example, in the sentence “the bottle is white” ( “la bottiglia è bianca” ), the word “white” is in its feminine form bianca to agree with the feminine word bottiglia (bottle) instead of its masculine form bianco .
Lastly, c’è (there is) and ci sono (there are) are also fixed expressions in Italian.
When to Use Avere
Avere is, of course, used to mean “to have,” but it is also used as an auxiliary for a compound tense (do not worry, we will explain that soon).
It is also used with very specific expressions, like to express age, hunger and thirst:
Maria ha 3 anni. (Maria is 3 years old.)
Io non ho fame. (I am not hungry.)
Luigi ha sete. (Luigi is thirsty.)
Further, avere is used in the expressions “to be in a hurry,” “to be afraid of,” “to need,” “to be sleepy,” “to feel like” and “to deal with.” Take a look at them:
Io ho fretta. (I am in a hurry.)
Mio figlio ha paura di questo film. (My son is afraid of that movie.)
Maria ha bisogno di una penna. (Maria needs a pen.)
Noi non abbiamo sonno. (We are not sleepy.)
Loro hanno voglia di andare. (They feel like going.)
Luigi ha a che fare con dei problemi ultimamente. (Luigi has been dealing with some problems lately.)
Essere and Avere in Compound Tenses
As we mentioned earlier, both avere and essere are also used as helper verbs (also known as “auxiliary verbs”) in compound tenses.
Common compound tenses include the passato prossimo (present perfect), trapassato prossimo (past perfect), futuro anteriore (future perfect), congiuntivo passato (past subjunctive) and condizionale passato (past conditional).
Essere as an Auxiliary
While avere acts as an auxiliary for a vast majority of Italian verbs, there is a select group of verbs that conjugate with essere in compound tenses.
These verbs include:
| Italian | English Translation |
|---|---|
| Arrivare | To arrive |
| Andare | To go |
| Uscire | To go out |
| Entrare | To enter |
| Venire | To come |
| Essere | To be |
| Partire | To leave |
| Stare | To stay, to be |
| Sparire | To disappear |
| Tornare | To come back/return |
| Nascere | To be born |
| Morire | To die |
| Rimanere | To remain |
If you are familiar with French, you will notice that some of these verbs are the same DR MRS VANDERTRAMP verbs that take être (to be) in the past tense.
Here are a few more examples:
Sono arrivato alle tre. (I arrived at three o’clock.)
Lui è tornato a casa. (He returned to the house.)
In addition to the above-mentioned verbs, reflexive verbs also take essere as their auxiliary. Reflexive verbs are those with a -si in their infinitive such as lavarsi (to wash oneself) or mettersi (to put on clothes).
Io mi sono lavato. (I washed myself.)
Loro si sono vestiti. (They got dressed.)
Avere as an Auxiliary
In the compound tenses, avere is used as the auxiliary for most verbs. These are verbs that generally take a direct or indirect object (which is another noun that follows the verb).
In these cases, avere is conjugated in its desired tense, and then the past participle is added.
Verbs that use avere include mangiare (to eat) and leggere (to read). Let’s check out their conjugations in the passato prossimo (the present perfect):
Mangiare (to eat) in the Present Perfect
| Italian | English Translation |
|---|---|
| Io ho mangiato | I ate |
| Tu hai mangiato | You ate |
| Lui ha mangiato | He ate |
| Lei ha mangiato | She ate |
| Noi abbiamo mangiato | We ate |
| Voi avete mangiato | You all ate |
| Loro hanno mangiato | They ate |
Leggere (to read) in the Present Perfect
| Italian | English Translation |
|---|---|
| Io ho letto | I read |
| Tu hai letto | You read |
| Lui ha letto | He read |
| Lei ha letto | She read |
| Noi abbiamo letto | We read |
| Voi avete letto | You all read |
| Loro hanno letto | They read |
Agreement with Essere
One last thing: when using essere as an auxiliary, the past participle must agree with the gender and number of the subject.
That means that the -o changes to an -a for past participles of feminine, singular subjects, to an -i for past participles of masculine, plural subjects and to an -e for past participles of feminine, plural subjects.
Io mi sono lavato. (I [masculine, singular] washed myself.)
Io mi sono lavata. (I [feminine, singular] washed myself.)
Loro si sono lavati. (They [masculine, plural] washed themselves.)
Loro si sono lavate. (They [feminine, plural] washed themselves.)
But be careful! This agreement happens only with essere and not with verbs that use avere as an auxiliary.
Practice Using Essere and Avere
That is a lot to take in, isn’t it? Well, lucky for you, there are loads of places to practice!
You can start off by practicing the conjugations of essere and avere in their present tenses on To Learn Free and Il Tavolo Italiano.
Next, look at essere on its own for some enhanced practice of this important verb with exercises from To Learn Free and Pro Profs.
You’ll also need to practice the passato prossimo with these two auxiliaries.
Round things off by seeing essere and avere being used in context by native speakers. One way to do this online is with authentic videos, like the ones on FluentU.
FluentU takes authentic videos—like music videos, movie trailers, news and inspiring talks—and turns them into personalized language learning lessons.
You can try FluentU for free for 2 weeks. Check out the website or download the iOS app or Android app.
P.S. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)
Now that we have gotten to know Italian’s parents better, we can really feel like we are a part of the big Italian family. Use your new knowledge on your road to fluency!
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
And One More Thing...
If you're as busy as most of us, you don't always have time for lengthy language lessons. The solution? FluentU!
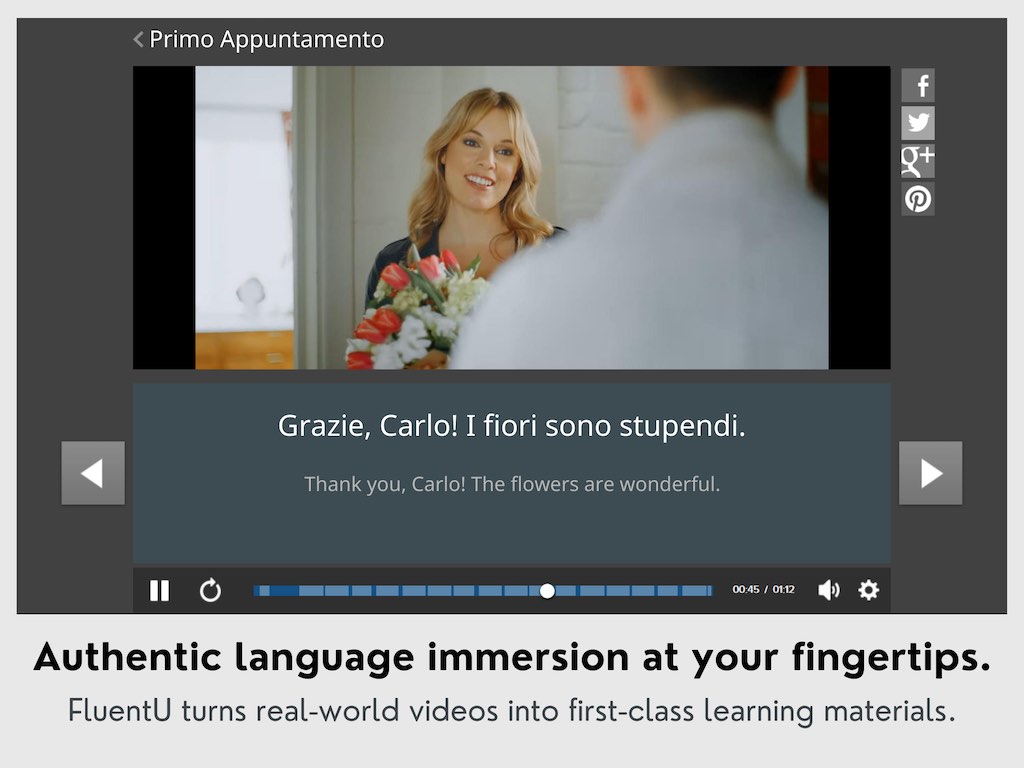
Learn Italian with funny commericals, documentary excerpts and web series, as you can see here:
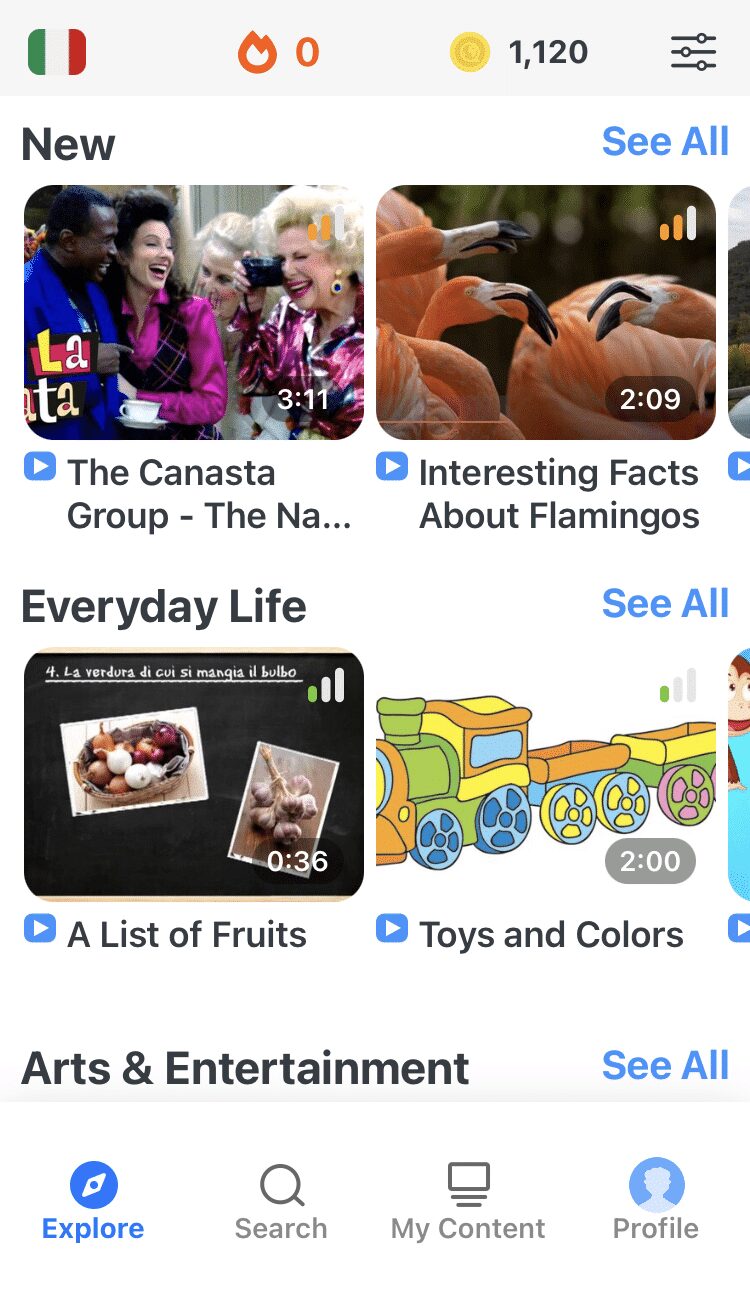
FluentU helps you get comfortable with everyday Italian by combining all the benefits of complete immersion and native-level conversations with interactive subtitles. Tap on any word to instantly see an image, in-context definition, example sentences and other videos in which the word is used.
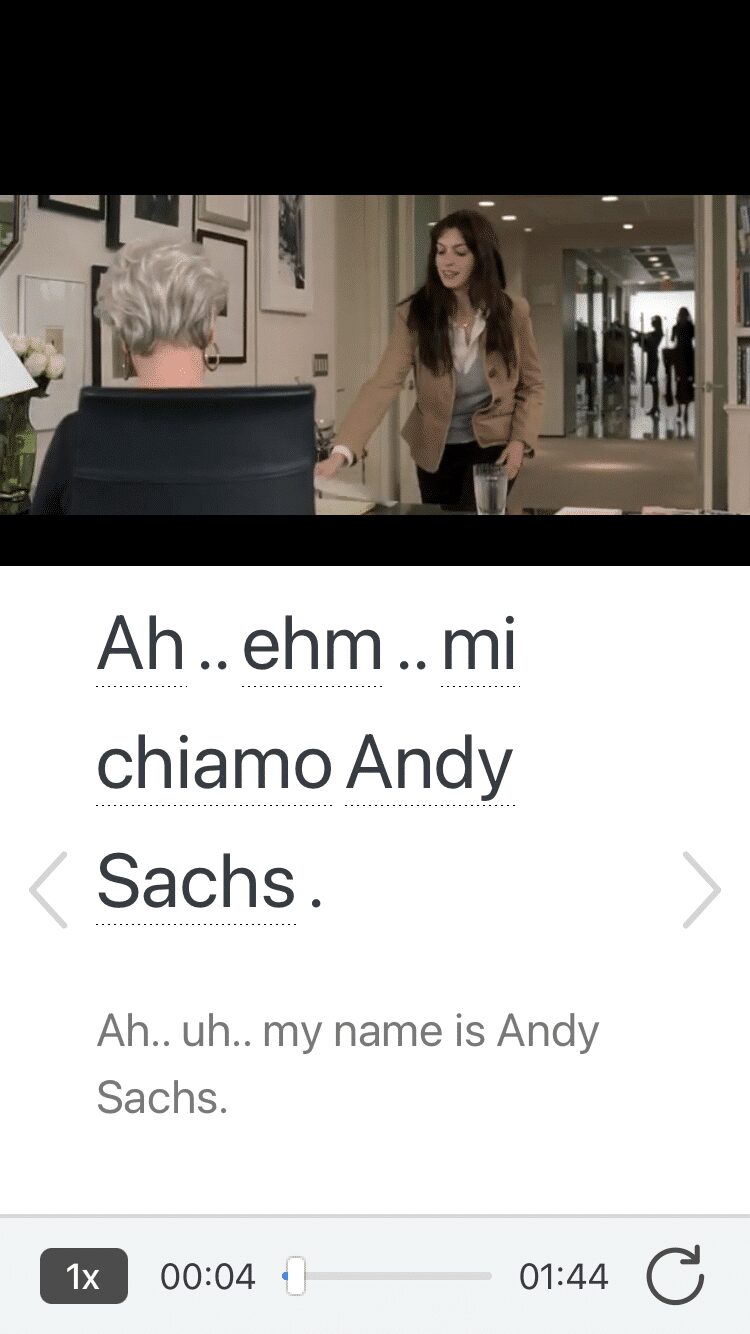
Access a complete interactive transcript of every video under the Dialogue tab, and review words and phrases with convenient audio clips under Vocab.
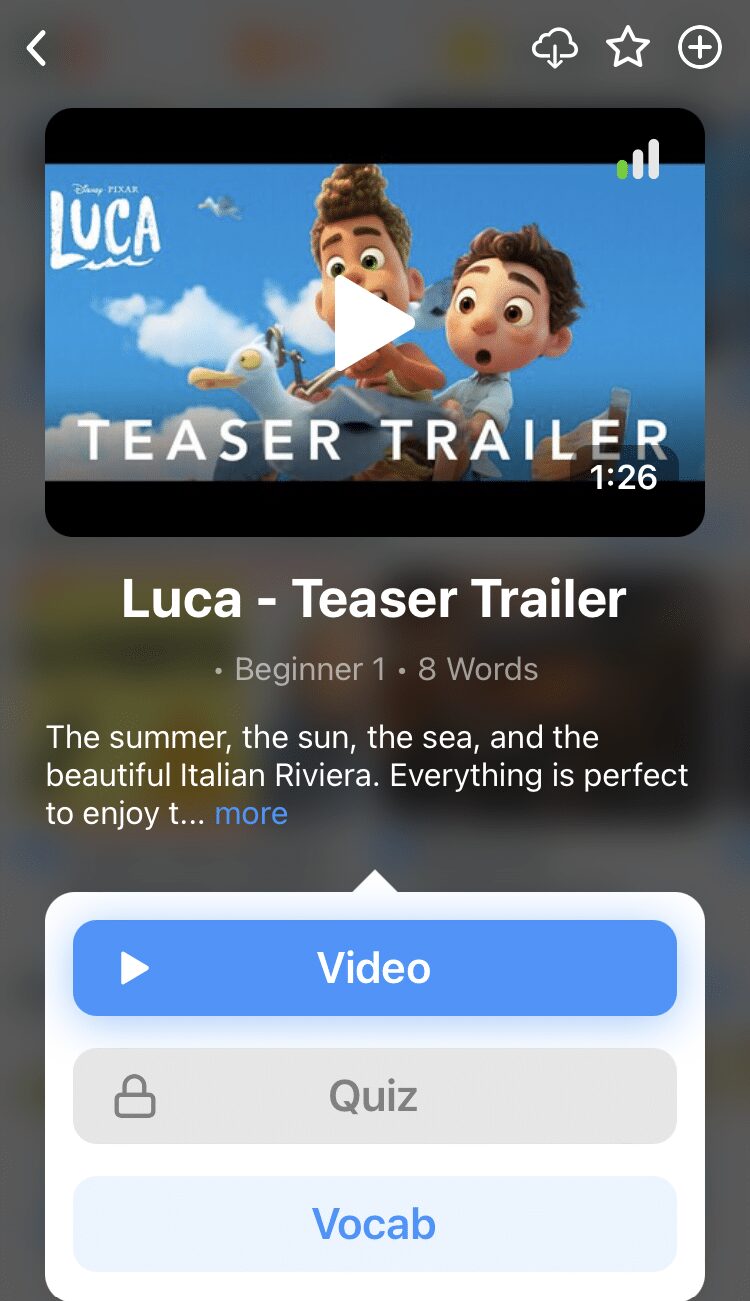
Once you've watched a video, you can use FluentU's quizzes to actively practice all the vocabulary in that video. Swipe left or right to see more examples of the word you’re on.
FluentU will even keep track of all the Italian words you’re learning, and give you extra practice with difficult words. Plus, it'll tell you exactly when it's time for review. Now that's a 100% personalized experience!
The best part? You can try FluentU for free with a trial.
Start using the FluentU website on your computer or tablet or, better yet, download the FluentU app from the iTunes or Google Play store. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)