Contents
- 1. Use Visual Elements to Memorize New Words
- 2. Write Something Every Day
- 3. Watch TV and Listen to Radio and Podcasts in the Target Language
- 4. Read Books at Your Actual Level
- 5. Branch Out from Textbooks
- 6. Learn What Interests You
- 7. Take Initiative and Personalize Your Learning Style
- And One More Thing...
How to Learn a Language by Studying Smarter, Not Harder

Just like most things in life, if you know the tips, tricks and hacks for learning something, the process usually goes much smoother, and much more successfully.
So if you’re looking for tips on how to learn a language effectively, read on. We’ve got seven key tips for you to consider on your language learning journey.
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
1. Use Visual Elements to Memorize New Words
Summary: Using visual elements is the best method to learn new words, as they trigger associations in our head, making it easier to remember permanently, not just learn by rote.
To understand and speak a language, several thousand words will be enough to get by in conversation and while reading modern writing. You’ll need more if you’re going to tackle more specialized or academic writing, or perhaps if you’re going to become a translator or interpreter. But we all have to start somewhere.
How do you know which words to learn and remember?
We live in the digital era when the internet surrounds us everywhere. So, check the list of most widely used words in the language you’re learning or download some apps that show you popular words, helping you to remember them along the way.
2. Write Something Every Day
Summary: Write blog posts, diary entries, shopping lists, notes to yourself or anything else that is already part of your daily life, but do it all in your target language. Using grammar in practice will improve your skills many times over.
Certainly, grammar is important, and no one is going to say that you shouldn’t learn it. But just writing sometimes, free of grammar concerns, is very helpful for language learning, too.
Regardless of the language, grammar is always tricky for non-native speakers (well, let’s be honest: it’s often tricky for native speakers, too). All those gerunds, tenses, infinitives and exceptions are useful when you write academic essays, do research or write professional emails. You need to build a foundation of great grammar in order to speak and write correctly.
However, if your primary goal is to communicate, prepare for a trip abroad or master just the basics, don’t stress about this too much. If you’re seriously turned off by the nitty gritty of grammar, don’t torture yourself trying to remember all the rules at once.
Many learners get discouraged by the idea of studying grammar and end up avoiding their daily practice. Don’t procrastinate. On days when grammar fills you with dread, treat yourself to some movies, games or music videos in your target language. Keep building familiarity with the language every day, and you’ll start learning grammar naturally.
Some educators recommend starting off with full immersion—constant exposure to the language through a diversity of authentic materials—and never cracking open a textbook or starting formal grammar study until you’ve developed basic proficiency in the language. You can always give this route a try!
3. Watch TV and Listen to Radio and Podcasts in the Target Language
Summary: To develop your listening skills, you can watch movies or TV shows with subtitles, listen to a radio show in your target language, play games, try to understand all words from your favorite songs and so on. Keep it fun and casual! Listening to TED lectures is always a good decision, too.
While learning a foreign language, we usually pay lots of undue attention to vocabulary and grammar. Our goal is to learn how to read, write and speak.
That’s all well and good, but we often forget about listening to a target language despite the fact that it’s key to understanding and communication.
Learners too often discover the hard way that speaking a language and understanding it aren’t the same thing.
Sometimes one can speak but can hardly understand native speakers at all while listening to songs or watching a movie in the target language. Never underestimate the importance of listening skills; you need to practice them on a daily basis.
4. Read Books at Your Actual Level
Summary: If you’re at the beginner level of learning, children’s books would be the best option for you. Intermediate and advanced learners can always try reading simplified versions of classics to learn some new words and grammar rules. If you’re pretty advanced, you can start tiptoeing towards the classics. Start with modern classics.
I bet your past or current language teachers have assigned you the task to read a book in the language you’re learning, make a vocabulary list of unknown words from it, learn them and discuss the book in the classroom afterward.
Such exercises are great unless your teacher asks you to read classic literature in the target language. They often don’t, and instead opt for abridged and otherwise simplified reading material.
Why?
First of all, it can be difficult to understand a plot and get pleasure from reading a book if you don’t know the meaning of most words. The “extensive reading” method encourages learners to choose texts where they know 95% of the words on any given page.
Secondly, books of classics may contain lots of archaic vocabulary (let’s take Shakespeare, for example). There’s no real need to learn all words from classics, as no one uses them in everyday language anymore.
However, many language learners make the mistake that teachers strive so hard to avoid—they dive into deep, complex literature and other texts that are well outside their reading level. They want to read what they want to read, even if they can’t read it! As you may already know, it can be very discouraging when you don’t understand most of what you’re reading.
You’re not giving yourself the chance to develop good reading habits. You won’t learn how to get into the flow of a native text if you’re constantly stopping to use your dictionary. You also won’t be able to pick up words via context if most of the language is way above your head (for the time being), and this kind of deductive work is critical for learning a language effectively.
5. Branch Out from Textbooks
Summary: Use all sorts of resources for learning your target language: newspapers, vlogs, novels, short stories, comments sections, advertisements, grocery lists—anything!
Going by the book is one of the biggest mistakes you can make while learning a foreign language.
The textbook can give you all the essential building blocks, but it can’t take you much farther.
Have you ever heard the people speaking in the audio files accompanying English textbooks? They’re speaking perfectly correct English, but they sound a bit forced and awkward at times. That’s because they’re reading a script designed for learners. It’s easy on the ears, and great for becoming familiar with the basics of language, but you’ll probably never hear a native speaker who talks quite like that.
Slang, idioms, jokes, regional dialects, pop culture references…they usually can’t be learned from standard textbooks. To really understand native speakers, you must learn casual language.
This doesn’t mean that you shouldn’t use textbooks at all. Some of them are worth trying, and one can find many reasons to use modern textbooks: They’re well-designed, they provide useful content and a road map for learning, they give lots of practice opportunities and they usually offer audio components.
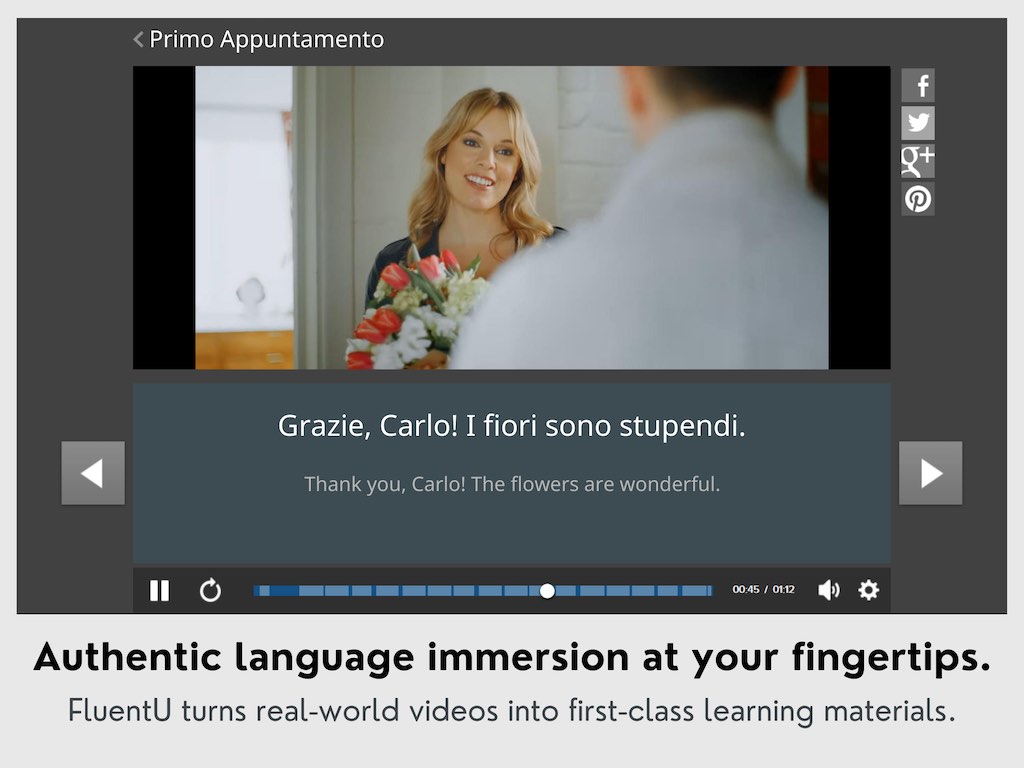
One thing you could try for learning with audio and video is a language learning program such as FluentU.
FluentU takes authentic videos—like music videos, movie trailers, news and inspiring talks—and turns them into personalized language learning lessons.
You can try FluentU for free for 2 weeks. Check out the website or download the iOS app or Android app.
P.S. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)
6. Learn What Interests You
Summary: Find materials about subjects that interest you. If you’re an accountant, that might be accounting statements from a large foreign company, or if you’re an art aficionado, read the latest museum exhibition guides in their original language.
Some learners aren’t super passionate about languages, and instead consider reaching fluency just another task to complete. It’s just another task on a life list, bucket list or resume building plan. There are a couple of noteworthy problems with this:
- It’s very difficult to pinpoint the exact moment you reach fluency, so you may never be able to check the “task complete” box.
- You don’t know a language just because you score all A’s and 100’s on your exams.
- You need to find some personal motivation coming from within to really master a language without ever losing focus.
You can’t just study for the test. Fluency doesn’t come until after you’ve put your language skills into action, spoken with natives for hours, listened to native speakers intently and followed their directions. You also need to learn the culture behind the language to a certain extent, or you’ll find a large gap between you and natives while communicating.
Not to mention, you have to constantly be updating your language knowledge. Languages change and develop all the time. Don’t miss a chance to learn the culture of those people whose language you learn, chat with your native speaker friends, watch movies, listen to songs, travel to countries and interact with locals.
7. Take Initiative and Personalize Your Learning Style
Summary: Seek out teachers and fellow students who learn like you like to learn and build a learning community, in real life or online.
This may be the most common mistake made by language learners. They rely on whatever course they’re taking, whether they’re taking it through a college, university or institute online, at home or abroad. This “reliance” comes in two forms:
- Relying on the course to give you all the material and exposure you need to learn.
- Holding the course or teacher responsible for your successes and failures.
When you learn a language, it’s good to have a teacher who will help and support you, but it doesn’t mean he or she can do everything for you. Teachers guide you—they can’t inject the language straight into your brain. It’s only you who’s responsible for your learning.
If you feel like the books and materials your school gives you aren’t effective or sufficient on their own, find a different textbook or other language learning materials to accompany the coursework. If the coursework doesn’t target your preferred learning style, learn how you learn best on your own time. If you learn best through music or visual cues, but simply don’t get enough of that in class, take care of yourself at home later.
Don’t only do your homework, study for tests and call it a day. Read and listen to your target language every day, communicate in it, go to language exchange clubs, make friends with native speakers and seek out new articles, blog posts, YouTube videos and more in that language. Become ravenous. Consume as much of the target language as you can on a daily basis.
Ask your school to assist you where needed, manage your emotions and try to stay motivated and optimistic.
If you don’t study properly and perform poorly on tests, take responsibility for this. If you ace all the reading and writing assignments but can’t speak without a heavy accent, then take responsibility for this and double up on speaking practice. The teacher and coursework can only get you so far.
Take these tips to heart and I think you’ll find your language learning journey moves faster than you ever thought it could. It’ll also be more fun!
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
And One More Thing...
If you dig the idea of learning on your own time from the comfort of your smart device with real-life authentic language content, you'll love using FluentU.
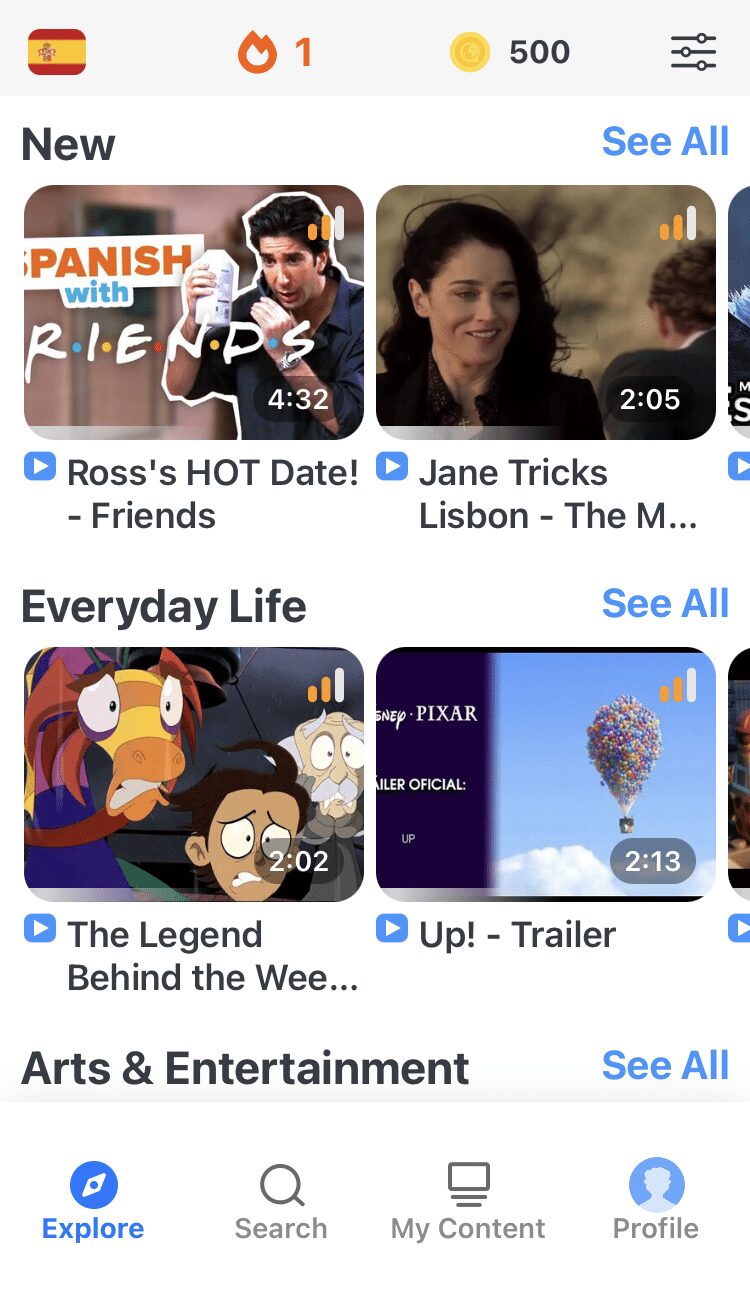
With FluentU, you'll learn real languages—as they're spoken by native speakers. FluentU has a wide variety of videos as you can see here:
With FluentU's Chrome extension, you can bring interactive learning tools directly to YouTube or Netflix, and even import your favorite YouTube videos directly into your FluentU account.
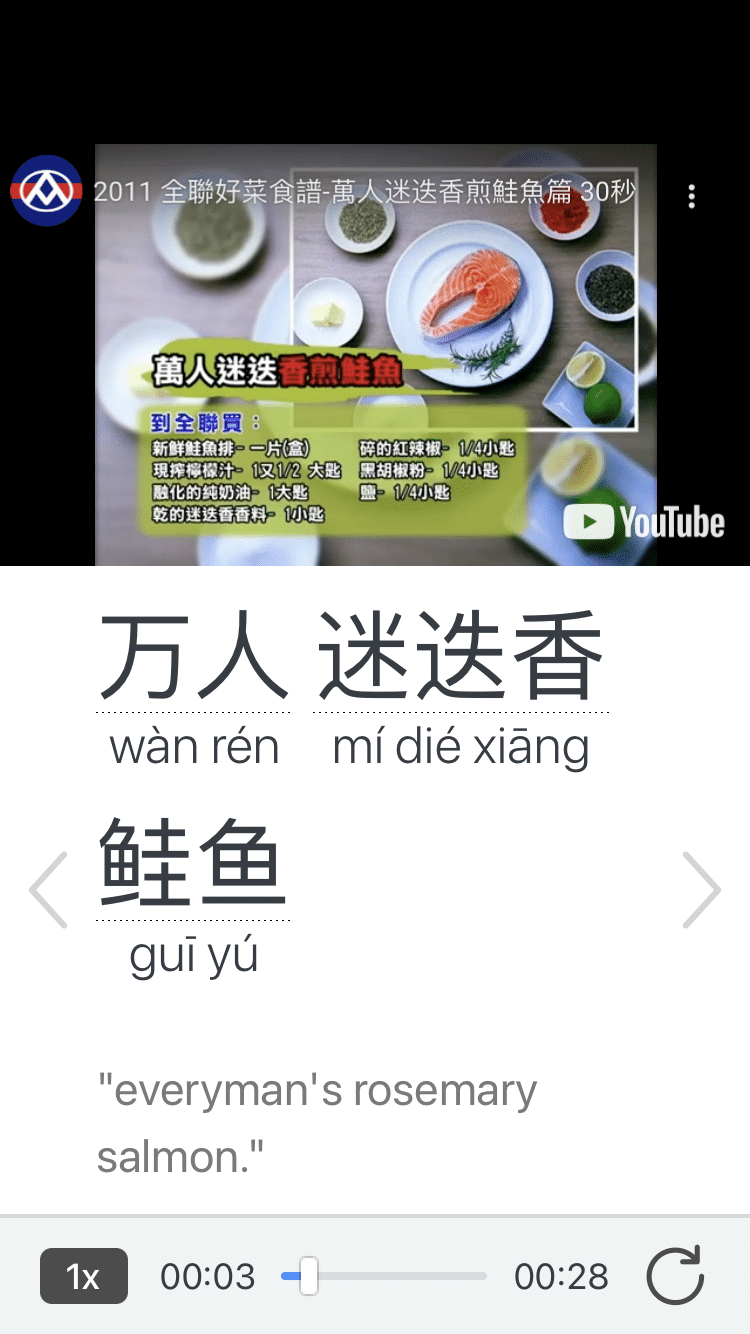
FluentU has interactive captions that let you tap on any word to see an image, definition, audio and useful examples. Now native language content is within reach with interactive transcripts.
Didn't catch something? Go back and listen again. Missed a word? Hover your mouse over the subtitles to instantly view definitions.
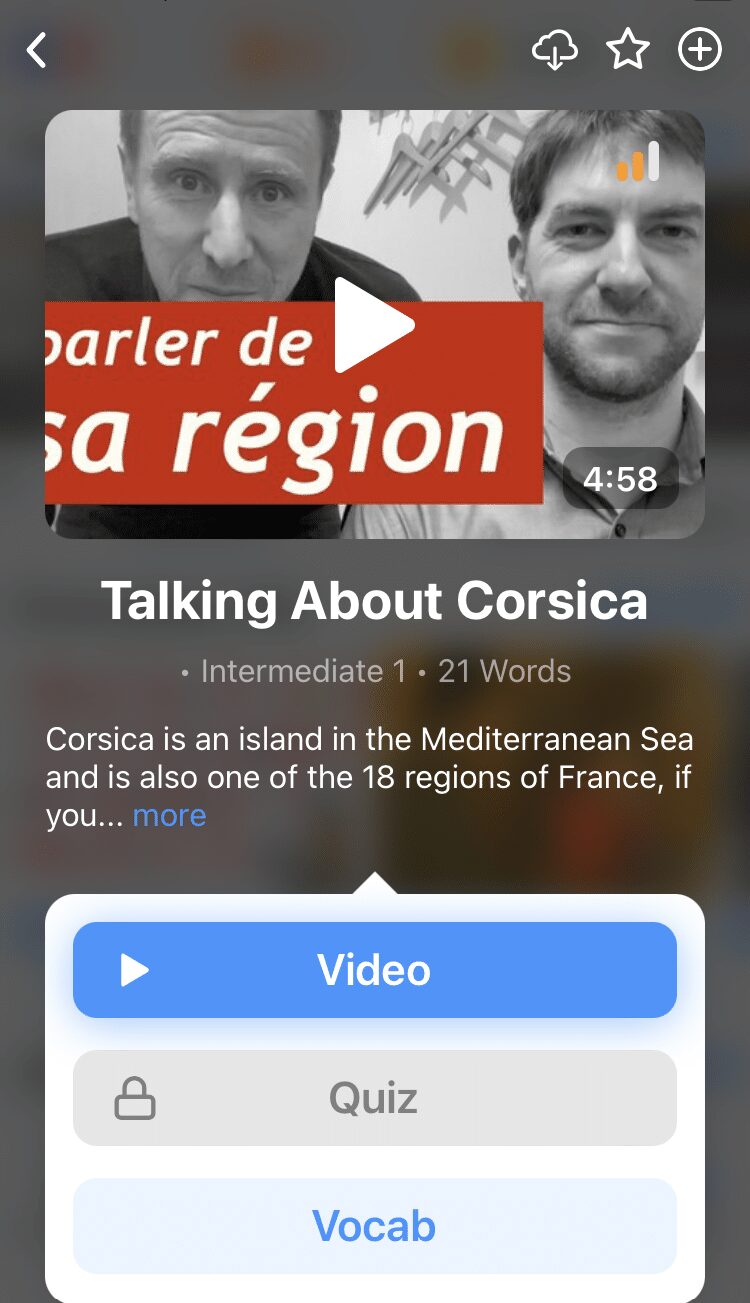
You can learn all the vocabulary in any video with FluentU's "learn mode." Swipe left or right to see more examples for the word you’re learning.
And FluentU always keeps track of vocabulary that you’re learning. It gives you extra practice with difficult words—and reminds you when it’s time to review what you’ve learned. You get a truly personalized experience.
Start using the FluentU website on your computer or tablet or, better yet, download the FluentU app from the iTunes or Google Play store. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)