Russian Dialects: Key Differences, Locations and Pronunciation

Russian as a whole is a relatively homogeneous language, with only slight variations in dialect and accent. However, it’s best to be prepared for the moment you come into contact with a native Russian speaker with an accent that varies from the standard.
That’s why familiarizing yourself with the differences between each regional variation is an important part of your Russian learning journey. See the guide below to learn about the different Russian dialects.
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
What’s the Difference Between Language, Dialect and Accent?
While there’s no perfect method for classifying the distinctions between these three concepts, there are simplistic explanations for each.
What Is a Language?
Language is often considered a standardized, ideal way of speaking. For example, Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) is regarded as the traditional form of Arabic, particularly for academic and religious purposes.
However, MSA is really used primarily for reading, and the only people who regularly speak MSA are news broadcasters.
What Is a Dialect?
Dialects are essentially sub-sets of a language, which typically dictate vocabulary and grammar usage.
For example, in Australia, a common greeting is “G’day mate. How ya going?”
This is how Aussies ask someone, “How are you?” This vocabulary choice is one example of what makes the Australian dialect different from other versions of English.
What Is an Accent?
Accent can be considered from two perspectives—some say an accent is how someone speaks a foreign language. It’s also how an individual pronounces words in their native language. It demonstrates which geographical, or in some cases, other social group, that person belongs to.
When a Frenchman, for example, speaks English, he likely has an identifiable French accent. Some nations are known for having countless dialects. For instance, while there’s one official language in China (Mandarin Chinese) there are over 300 dialects used throughout the country.
Russian is not known for having any stand-out idiosyncrasies, but it’s worth discussing language, dialects and accent in the Russian context so that you’re well-prepared for what you might encounter in your Russian studies.
The 3 Russian Dialects
To be a well-informed Russian language student, there are three Russian dialects you should be aware of—Northern, Central and Southern.
Северный говор (Northern Dialect)
Geographical region: north of Moscow, in области (districts) such as Nizhny Novgorod, St. Petersburg, Murmansk, Siberia and the Far East.
Northern Russian is discernable due to the speakers’ tendency to pronounce an obvious and long O. This is referred to as оканье , or okanie. Next time you hear a Northerner say the word много (many), pay attention because they’ll likely pronounce it with two long Os similar to the way Bulgarians pronounce it.
Another recognizable aspect of Northern Russian is the pronunciation of Ч (ch) as Ц (ts). Печка (stove), which is normally pronounced with a “ch” sound, may sound more like “petska” in the north.
Среднерусский говор (Central Dialect)
Geographical region: Moscow and most major cities.
As a general rule, the central dialect is intended to bridge the gap between the Northern and Southern dialects.
It’s the “default” or “standard” form of Russian. As such, most people can understand someone from Moscow or St. Petersburg with little difficulty.
However, speech patterns are more similar between Vologda and Vladivostok, which is 6,000 miles to the east, than between Moscow and Ryazan, located barely 135 miles south.
The Central dialect is also considered the literary or cultural norm of Russian.
One means of explaining the Central dialect is that it marries the vowel system of the Southern dialect with the consonant system of the Northern.
The most noticeable vowel inclination is showcased in the central use of аканье , or akanie. Akanie is the standard Russian pronunciation of both O and A, as A when both vowels are unstressed. For instance, много (many) is pronounced with a short A at the end in the Central dialect.
Южный говор (Southern Dialect)
Geographical region: Belgorod, Bryansk, Kaluga, Kursk, Lipetsk, Oryol, Ryazan, Smolensk, Tambov, Tula, Voronezh.
One prominent characteristic of the Southern dialect is the fricative G.
Rather than pronouncing Г (g sound), it’s pronounced as if it was a Х (h sound). For example, снег (snow) is pronounced sneH (instead of sneG), which is more in line with the Belarusian pronunciation, while нога (leg) is pronounced naHa, as the Ukrainians say it (instead of naGa).
The Southern dialect also includes яканье , or yakanye, which causes O, E and A to all be pronounced as a hard A sound (such as in the English word “bat”) before a stressed syllable. The most conspicuous example is несли (to carry), which is pronounced nyAslee (instead of nyeslee).
East Slavic Languages
Slavic languages can be broken into three branches: West Slavic (Czech, Slovak and Polish), South Slavic (Serbo-Croatian, Bulgarian and Macedonian) and East Slavic (Russian, Ukrainian and Belarusian). East Slavic languages all use the Cyrillic script.
During the existence of the Soviet Union, Ukrainian and Belarusian were both classified as dialects of Russian.
Belarusian is most closely related to Ukrainian, but shares 75% of mutual intelligibility with Russian.
However, Russian is still the main language in Belarus, being spoken by over 70% of Belarusians at home. Nevertheless, there are some noticeable differences between Russian, Ukrainian and Belarusian which you should be able to notice.
Check out the video below to hear some of them!
Why Do You Need to Know About Russian Dialects?
As with most countries and languages, you’ll find minor geographical differences in the ways people speak, but until you reach a high level of fluency, you’re unlikely to notice it.
The most important time to consider Russian dialects is probably when you’re selecting a tutor. There are various platforms from which you can select a tutor. And one-on-one online tutoring can really take your language to the next level. But keep in mind where your tutor is from.
I spent two years taking online Russian classes from a tutor in Kiev and was surprised when I visited St. Petersburg and was asked if I had learned Russian in Ukraine. At that point, I hadn’t even visited Ukraine, yet the slight accent my tutor had rubbed off on me. This isn’t a big deal in the grand scheme of things, but native Russian speakers may pick up on any peculiarities in your speech.
Finally, for more advanced students—or very ambitious novices—here’s an excellent video presented in Russian that describes in detail the various distinctions you might hear in the language!
And there you have it, the three primary Russian dialects you should be aware of! Are you particularly fond of one over the others? Or perhaps you’ve just now noticed that you already have a region-specific accent? Hear more examples by listening to native Russian content and media, like the videos on FluentU.
FluentU takes authentic videos—like music videos, movie trailers, news and inspiring talks—and turns them into personalized language learning lessons.
You can try FluentU for free for 2 weeks. Check out the website or download the iOS app or Android app.
P.S. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)
Remember, no matter where you go in Russia, you’ll be understood. So don’t let different Russian dialects discourage you!
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
And One More Thing…
If you’re like me and prefer learning Russian on your own time, from the comfort of your smart device, I’ve got something you’ll love.
With FluentU’s Chrome Extension, you can turn any YouTube or Netflix video with subtitles into an interactive language lesson. That means you can learn Russian from real-world content, just as native speakers actually use it.
You can even import your favorite YouTube videos into your FluentU account. If you’re not sure where to start, check out our curated library of videos that are handpicked for beginners and intermediate learners, as you can see here:
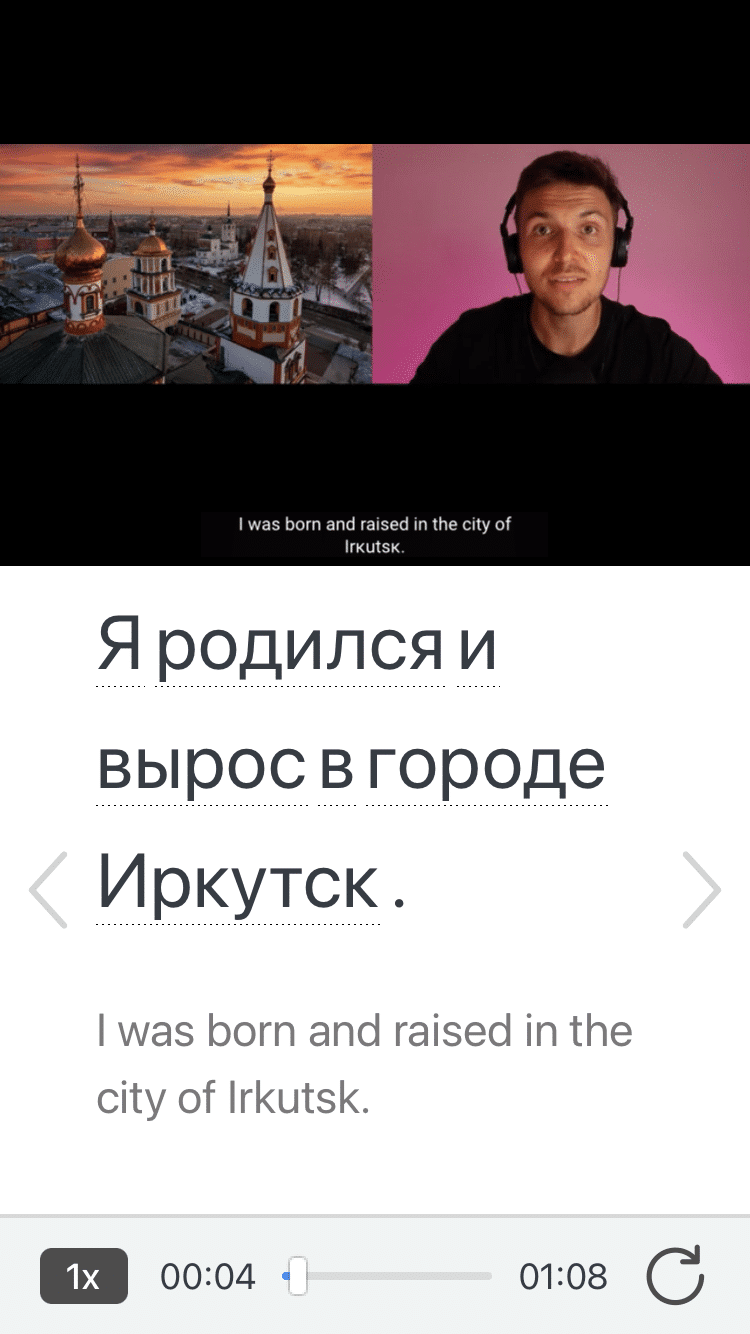
FluentU brings native Russian videos within reach. You can watch videos with dual-language subtitles and hover over any word to see its meaning along with an image, audio pronunciation, and grammatical information.
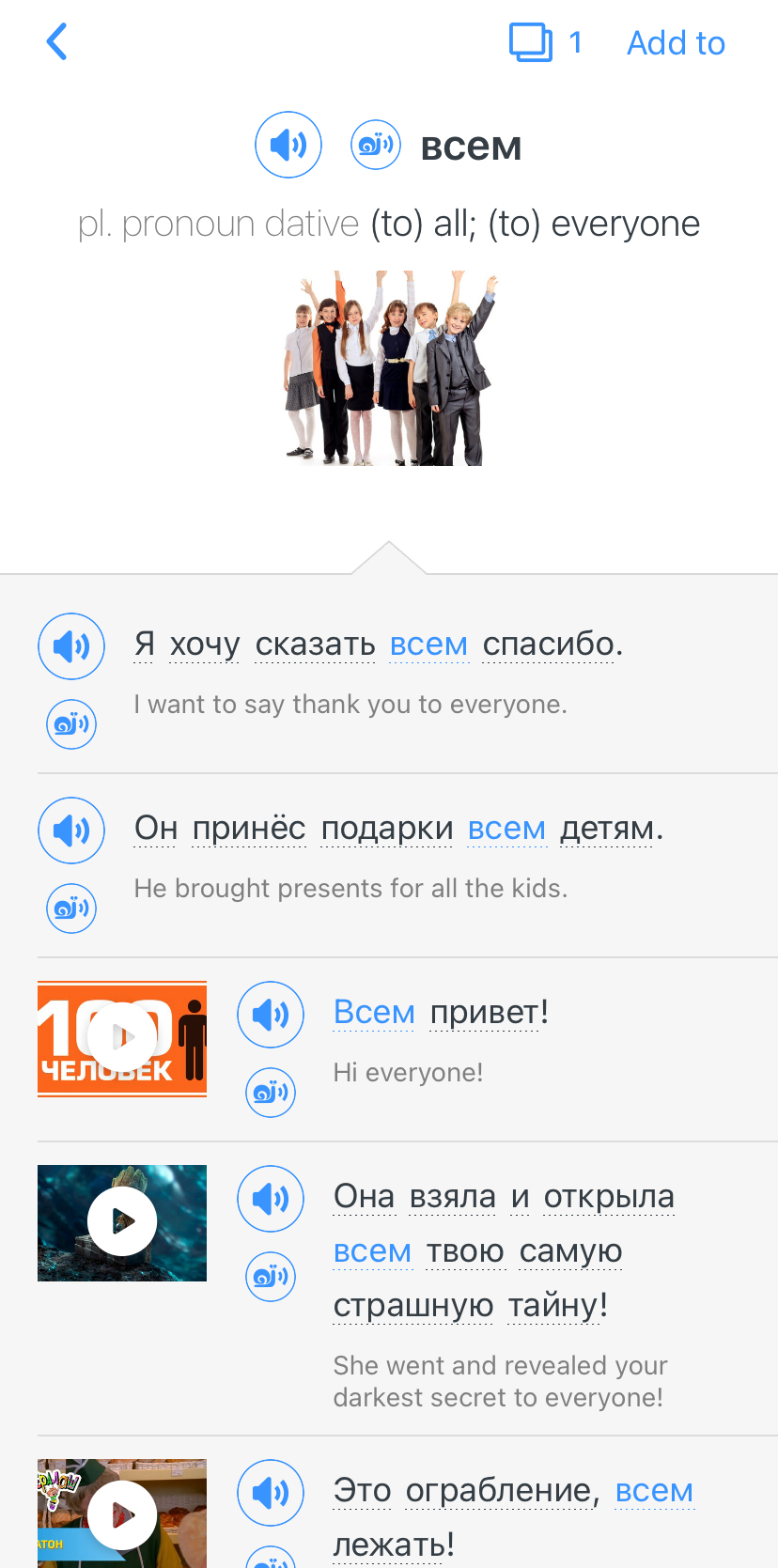
Click on a word to see more examples where it's used in different contexts. Plus, you can add new words to your flaschards! For example, if I tap on всем, this is what pops up:
Want to make sure you remember what you've learned? We’ve got you covered. Each video comes with exercises to review and reinforce key vocab. You’ll get extra practice with tricky words and be reminded when it’s time to review so nothing slips through the cracks.
The best part? FluentU tracks everything you’re learning and uses that to create a personalized experience just for you. Start using the FluentU website on your computer or tablet or, better yet, download our app from the App Store or Google Play.
Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)