52 Spanish Essay Phrases for Your AP Exam

In order to do well on the AP Spanish exam’s free-response section, you must be able to write a persuasive essay based on three Spanish-language sources.
Here we’ve put together a list of 52 vocabulary words and essays phrases that will come in handy for making and supporting arguments in your AP Spanish essays.
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
Handy Essay Phrases for Writing a Strong Spanish AP Composition
Starting your essay
Para empezar – To begin with
Hoy en día – Nowadays…
Hoy en día, las personas están en Internet hasta ocho horas por día. (Nowadays, people are on the Internet up to eight hours per day.)
A manera de introducción – We can start by saying…
Como punto de partida– As a starting point
Al principio – At the beginning…
En primer lugar – To start…
Empecemos por considerar – Let’s begin by considering…
Agreeing and disagreeing
Estoy de acuerdo/No estoy de acuerdo — I agree/I disagree
Estoy de acuerdo con lo que dice el autor. (I agree with what the author says.)
No estoy de acuerdo con la idea principal de la fuente número dos. (I disagree with the main idea of source number two.)
En mi opinión — In my opinion
En mi opinión, los jóvenes deberían comer más sano. (In my opinion, young people should eat healthier.)
La verdad es — The truth is
La verdad es que todavía hay mucha desigualdad en los Estados Unidos. (The truth is there is still a lot of inequality in the United States.)
Es verdad — It’s true
Es verdad que las redes sociales pueden ser peligrosas. (It’s true that social media can be dangerous.)
Es falso — It’s false
Hay gente que dice que las redes sociales son peligrosas, pero esto es falso. (There are people who say that social media is dangerous, but this is false.)
Me parece/No me parece — It seems to me/It doesn’t seem to me
Me parece bien que los niños asistan a colegios bilingües. (I think it’s a good idea that children attend bilingual schools.)
No me parece bien que los niños asistan a colegios bilingües. (I don’t think it’s a good idea that children attend bilingual schools.)
Remember that since me parece implies an opinion or emotion, you must conjugate the verb in the subjunctive tense.
(Yo) pienso que — I think that
Yo pienso que no hay nada más importante que la familia. (I think that there is nothing more important than family.)
(Yo) creo que — I believe that
Yo creo que todos los adolescentes deberían aprender a tocar un instrumento. (I believe that all adolescents should learn to play an instrument.)
Stating an opinion
The following phrases all have the same structure: Es + adjective + que.
This structure is similar to the English “It’s [adjective] that…” and is great for expressing and supporting opinions in a strong and confident manner. Here are some phrases that are especially useful when making and defending claims in a persuasive essay:
Es evidente que — It’s evident that
Es claro que — It’s clear that
Es cierto que — It’s certain that
Es obvio que — It’s obvious that
Es importante que — It’s important that
Es necesario que — It’s necessary that
Es probable que — It’s probable that
Es dudoso que — It’s doubtful that
For some of these phrases, the verb following the word que must be conjugated in the indicative, while others require the subjunctive. A good rule of thumb is that when implying that something is certain, use the indicative. When expressing doubt or expressing some other emotion, use the subjunctive.
On this list, evidente, claro, cierto and obvio use indicative verbs, and importante, necesario, probable and dudoso use subjunctive verbs.
Es cierto que nuestro clima está cambiando. (It is certain that our climate is changing.)
Es importante que la gente sepa hablar más de un idioma. (It’s important that people know how to speak more than one language.)
Supporting an opinion
These words will help you refer to your three sources, which contain information that will help you support your argument. This section also contains transition words to connect one part of your argument to the next.
Según — According to
Según el autor… (according to the author…)
La fuente — The source
Según la fuente numero 1… (According to source number one…)
El tema — The theme/topic
Esto es un tema muy importante. (This is a very important topic.)
Mostrar — To show
La fuente muestra la importancia de la diversidad. (The source shows the importance of diversity.)
Remember, mostrar is an o-ue stem-changing verb—pay attention to conjugation!
Demostrar — To demonstrate
La tabla demuestra que muchos jóvenes en España juegan al fútbol. (The table demonstrates that many youths in Spain play football.)
Demostrar is also an o-ue stem changing verb. Luckily for you, it follows the exact same conjugation rules as mostrar!
Indicar — To indicate
La tabla indica que hay muchas familias pobres en ese barrio. (The table indicates that there are many poor families in that neighborhood.)
Apoyar — To support
Estos datos apoyan la idea de que el clima está cambiando. (This data supports the idea that the climate is changing)
Sin duda — Without a doubt
Sin duda, el cambio climático es el problema más grave que enfrenta nuestra planeta. (Without a doubt, climate change is the most serious problem that our planet faces.)
Contrasting (or comparing)
Por otra parte — On the other hand
Es importante que la economía crezca, pero por otra parte, tenemos que cuidar el medio ambiente. (It’s important that the economy grows, but on the other hand, we have to care for the environment.)
Aunque — Even though/Although
Aunque is followed by an indicative verb when the outcome is known, but a subjunctive verb when the outcome is speculative.
Aunque cuesta mucho dinero, tenemos que buscar una solución. (Even though it costs a lot of money, we have to search for a solution.)
Aunque cueste mucho dinero, tenemos que buscar una solución. (Even though it may cost a lot of money, we have to search for a solution.)
Al igual que — Just like
Al igual que en los años 40, hoy en día hay mucha gente que no quiere ayudar a los refugiados de guerra. (Just like in the 40s, today there are many people who don’t want to help war refugees.)
Tanto… como… — …as well as…
Fill in this phrase with two nouns to emphasize that you’re talking equally about two different things.
Tanto chicos como chicas deberían aprender a cocinar, limpiar, coser y cuidar a los bebés. (Boys as well as girls ought to learn how to cook, clean, sew and care for babies.)
Sino — But rather
Remember that Spanish has two translations for the English word “but.” The word sino is like the English phrase “but rather,” used to introduce an alternative.
En comparación — In comparison
En comparación, la fuente número 2 indica que hay más obesidad en Estados Unidos que en España. (In comparison, source number 2 indicates that there is more obesity in the United States than in Spain.)
Leer no es una pérdida de tiempo, sino una manera de aprender y de conocer otras culturas. (Reading isn’t a waste of time, but rather a way to learn and understand other cultures.)
Transitional phrases
Además — Additionally
This word is usually seen at the beginning of a sentence, and it’s useful for transitioning from one idea or argument to another.
Además, es evidente que la tecnología nos ayuda mucho. (Additionally, it’s evident that technology helps us a lot.)
Sin embargo — However
This is another good transition word. In your essay, you may want to present an alternate argument and then explain why you disagree with it. Sin embargo is very helpful for this.
Obviamente, estudiar es muy importante. Sin embargo, es necesario que los adolescentes tengan tiempo para jugar con sus amigos. (Obviously, studying is very important. However, it’s necessary that teenagers have time to play with their friends.)
Por lo cual — For this reason/That’s why/Which is why
This phrase is used in the middle of a sentence to connect ideas.
La Amazonía tiene un alto nivel de biodiversidad, por lo cual la conservación de esta región debe ser una prioridad. (The Amazon has a high level of biodiversity, which is why the conservation of this region must be a priority.)
Changing topics
Sobre un tema relacionado — On a related topic
Sobre un tema relacionado con la inteligencia artificial, se están llevando a cabo investigaciones para mejorar la capacidad de aprendizaje de los algoritmos de machine learning. (Regarding a topic related to artificial intelligence, research is being conducted to enhance the learning capacity of machine learning algorithms.)
Cuando se trata de – When it comes to
Relacionado con esta idea — Related to this idea
Una idea similar es — A similar idea is
Una idea similar es utilizar la realidad virtual como herramienta educativa para mejorar la experiencia de aprendizaje de los estudiantes. (A similar idea is to use virtual reality as an educational tool to enhance the learning experience of students.)
Ahora estoy pasando a — Now moving onto
Concluding your essay
In your final paragraph, you’ll want to provide a summary of your main argument and your main supporting points. You can use the following helpful phrases:
En conclusión — In conclusion
En resumen — In summary
En fin — Finally
En conclusión,/En resumen,/En fin, las tres fuentes muestran que la contaminación del aire es un problema muy grave para todo el mundo. (In summary, the three sources show that air pollution is a very serious problem for the whole world.)
After summarizing your essay, you’ll want to restate your main argument in a succinct, strongly-worded sentence. Start with these phrases:
Por estas razones — For these reasons
Por eso — That is why
Así que — Therefore
Entonces — So
Por estas razones,/Por eso,/Así que/Entonces, afirmo que los adolescentes no deberían usar las redes sociales. (For these reasons, I affirm that teenagers should not use social media.)
How to Prepare for the AP Spanish Essay
In many ways, preparing for the free-response section is the same as preparing for the rest of the AP exam.
It involves studying grammar and vocabulary, and it also means immersing yourself in the Spanish language as much as possible.
There are also some targeted ways to practice for the free-response section.
- Do practice exams and read sample essays. The College Board has posted the full AP exams from the last several years. Try to read the sources and write the essay in the allotted 55 minutes. When you’re done, go back and slowly revise your essay for errors in grammar, spelling and logic. After that, you can also check out the grading rubric provided by the College Board and several sample persuasive essays. Try to compare your essay against the rubric and the samples to see how you can improve your writing.
- Practice summarizing and analyzing Spanish-language sources. Remember all those great resources listed above? Well, it’s not enough to just read or listen to them. The whole point of the presentational essay is to measure your ability to summarize, synthesize and argue. So, after you read or listen to a Spanish-language source, take five minutes to summarize it—on paper. Identify the main argument, and then make a bulleted list of important points. Finally, write a few sentences summarizing your personal opinion.
- Learn targeted vocabulary for talking about opinions and arguments. Is there anything more frustrating than knowing exactly what you want to say, but not having the vocabulary to say it? This article lists many crucial vocabulary words for expressing and supporting opinions in persuasive essays. Using these words and phrases will help make your writing flow more smoothly, and allow you to argue with more credibility.
- Use authentic content to immerse yourself so you get used to thinking in Spanish. A virtual immersion program like FluentU can help you get going with a bit more structure.
FluentU takes authentic videos—like music videos, movie trailers, news and inspiring talks—and turns them into personalized language learning lessons.
You can try FluentU for free for 2 weeks. Check out the website or download the iOS app or Android app.
P.S. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month)

You can also find some great info on great news outlets, podcasts, YouTube channels and blogs—all in Spanish. Even following some Spanish Twitter feeds or listening to Spanish music can be a great way to work a little language practice into your day.
What Are the Details of the AP Spanish Essay?
The free-response section of the exam is meant to test your ability to communicate with others in spoken and written Spanish.
There are two essays in the free-response section. The interpersonal essay asks you to respond to an email. The presentational essay tests how well you can draw information from Spanish-language sources, form an argument and write formally. This second essay is a little less straightforward, so we’ll walk you through it here.
So, how does it work?
The presentational essay is based on three sources. Two of them are written sources and one is an audio source.
These sources can be just about anything: Advertisements, articles, infographics, letters, maps, interviews, radio programs, podcasts and conversations are just some examples of the types of sources you may encounter.
You’ll have about 55 minutes to complete this particular essay. First, you’ll have six minutes to read the prompt and the two written sources, and then you’ll hear the audio source twice. Finally, you’ll have 40 minutes to plan and write your essay.
The essay is graded on the basis of Spanish language skills like reading, listening, writing and grammar—but it’s also based on your general ability to analyze the sources and make a strong, coherent argument.
Of course, learning vocabulary and essay phrases is just one way to prepare for the free-response section.
Remember to expose yourself to as many Spanish-language sources as you can before test day, and don’t forget to think critically about those sources as you read them!
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
And One More Thing…
If you've made it this far that means you probably enjoy learning Spanish with engaging material and will then love FluentU.
Other sites use scripted content. FluentU uses a natural approach that helps you ease into the Spanish language and culture over time. You’ll learn Spanish as it’s actually spoken by real people.
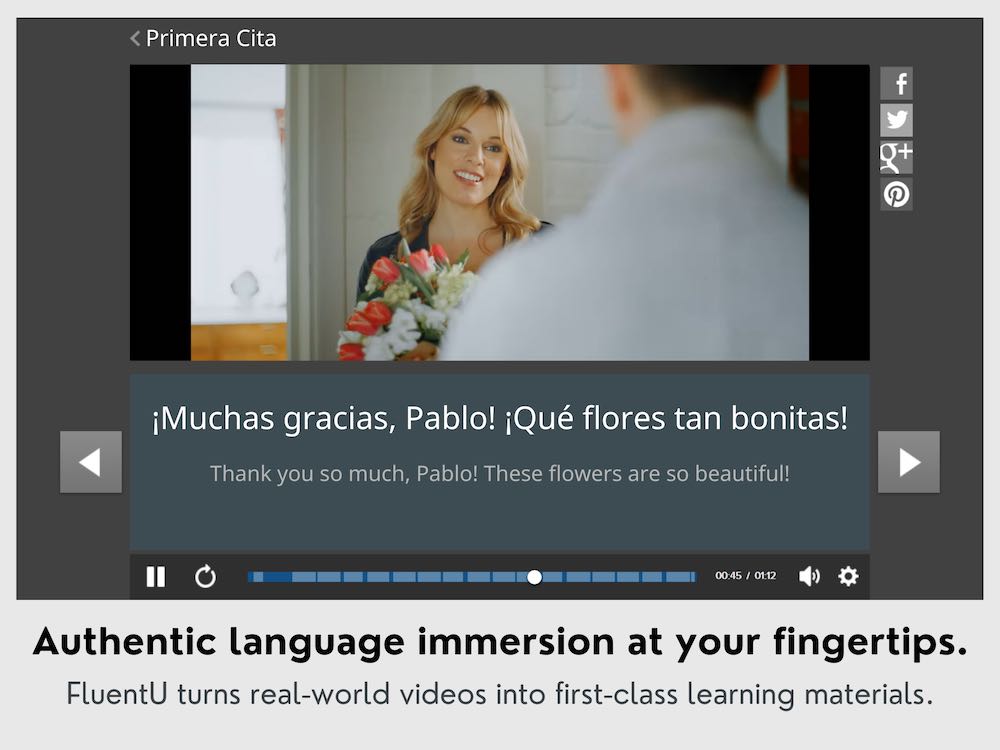
FluentU has a wide variety of videos, as you can see here:
FluentU brings native videos within reach with interactive transcripts. You can tap on any word to look it up instantly. Every definition has examples that have been written to help you understand how the word is used. If you see an interesting word you don’t know, you can add it to a vocab list.

Review a complete interactive transcript under the Dialogue tab, and find words and phrases listed under Vocab.
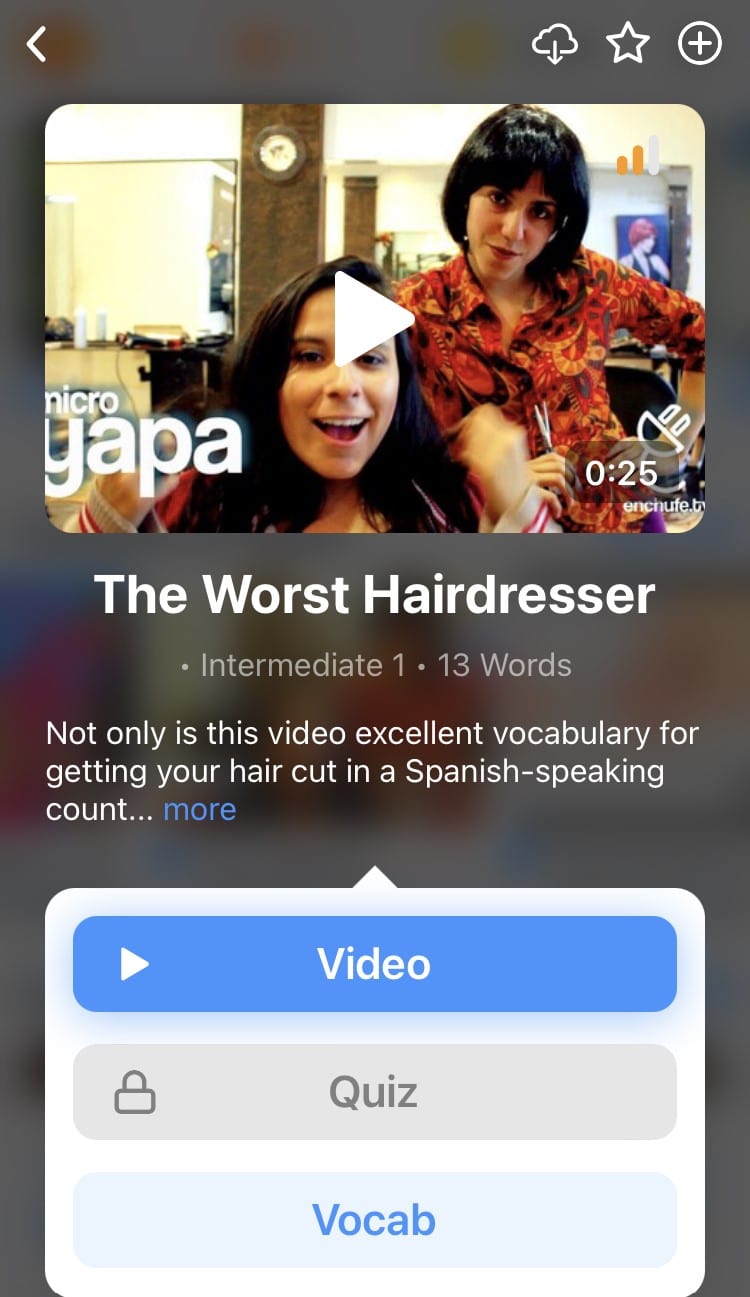
Learn all the vocabulary in any video with FluentU’s robust learning engine. Swipe left or right to see more examples of the word you’re on.
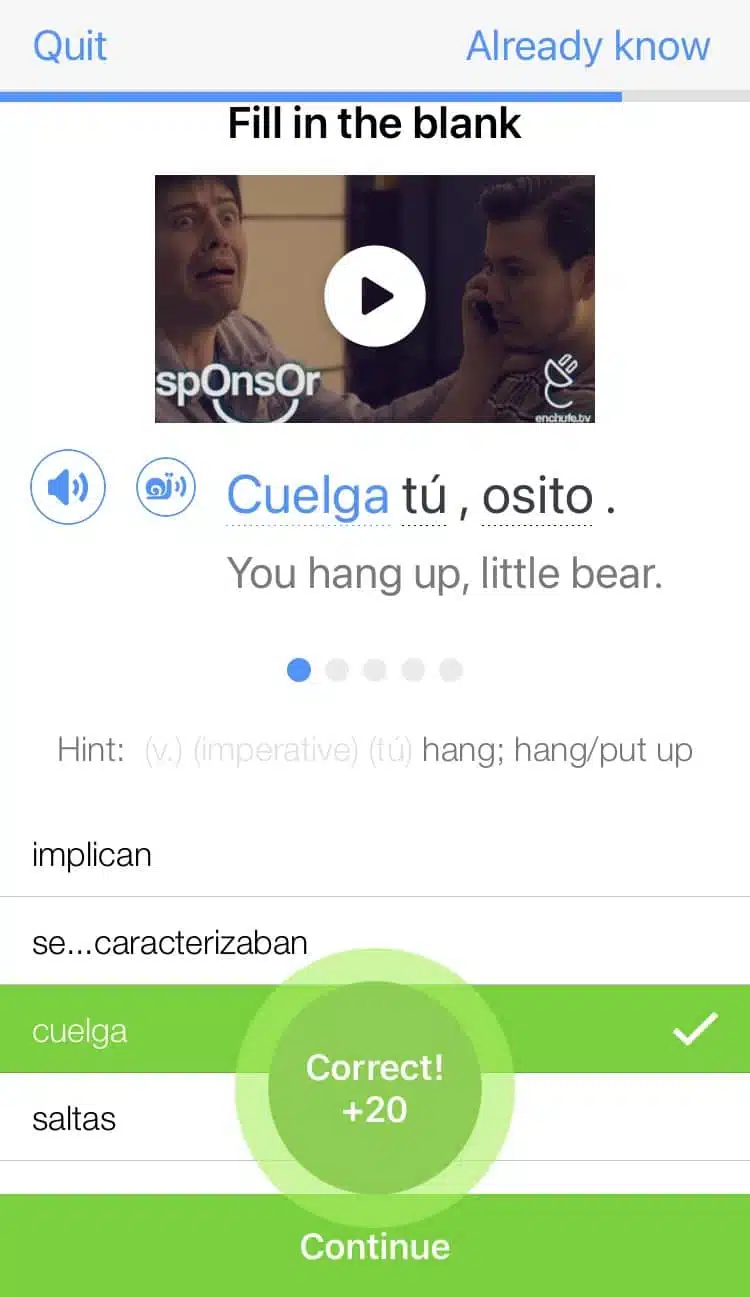
The best part is that FluentU keeps track of the vocabulary that you’re learning, and gives you extra practice with difficult words. It'll even remind you when it’s time to review what you’ve learned. Every learner has a truly personalized experience, even if they’re learning with the same video.
Start using the FluentU website on your computer or tablet or, better yet, download the FluentU app from the iTunes or Google Play store. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)